Table of Contents
The world of e-commerce is becoming more competitive every day. With this rapid increase in competition, businesses must harness strategic methodologies to stay ahead and sustain growth.
Among these strategies, cross-selling, and upselling are proven and effective methods to boost sales and customer loyalty. This guide will dive into these techniques, unravelling their definitions, differences, real-life examples, pros, cons, and tips for an effective strategy.
The importance of cross-selling vs upselling tactics in e-commerce can’t be overstated. Both strategies target customers who have already shown interest or already purchased, significantly increasing their chances of buying more.
Further down, you will learn how to maximize e-commerce growth using these strategies, which when applied correctly, enhance customer relationships, improve customer lifetime value (CLTV), and ultimately yield higher revenue.
Let’s start!
How Cross-selling and Upselling Leads to E-commerce Growth?
Cross-selling and upselling strategies are not just about increasing order values; they are key contributors to overall e-commerce growth. First, these strategies foster deeper relationships with customers. When customers feel you understand their needs and can meet them, this builds trust and loyalty.
Additionally, cross-selling or upselling to existing customers is more cost-effective than acquiring new ones. This can positively impact your overall e-commerce growth by freeing up resources to invest in other growth areas.
In the long term, cross-selling and upselling can lead to higher customer lifetime value (CLTV), as these customers are likely to return and make further purchases. Also, it improves customer satisfaction as they discover additional worthwhile products or better alternatives to past purchases.
Understanding the Basics of Cross-selling vs Upselling
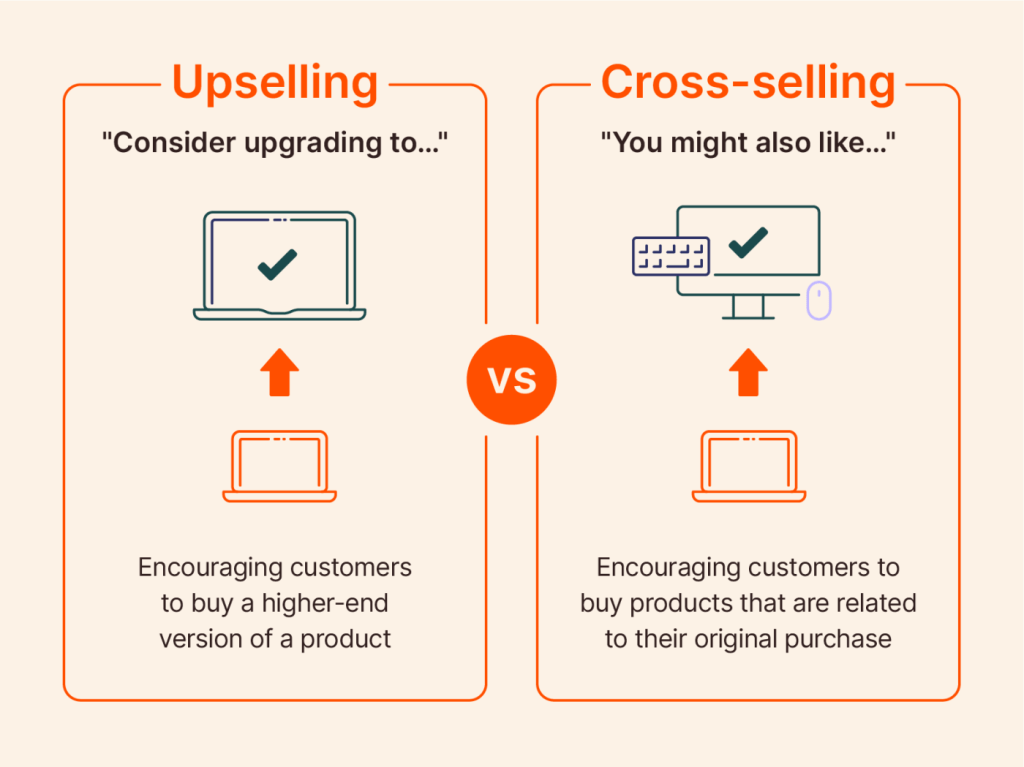
Often, the terms cross-selling and upselling are used interchangeably. However, they represent unique selling strategies. Cross-selling involves recommending additional, complementary products to customers based on their current purchase.
This marketing strategy often aims to increase the overall purchase value by offering items that perfectly supplement the customers’ initial choice. For example, a customer buying a mobile phone might be cross-sold a mobile case or earbuds.
In contrast, upselling refers to encouraging customers to purchase a more expensive version of a product or add extras to their purchase for a better variant or service. You’re essentially persuading a customer to upgrade their product or add services that make the more expensive version seem more valuable, thus increasing their spending. For example, suggesting a premium paint finish on a new car would be an upsell.
Key differences between these strategies involve their application. While cross-selling targets to widen the purchase scope by suggesting complementary products, upselling aims to elevate the product’s version or service being purchased, thereby increasing the spending and shopping cart value directly.
What is Cross-Selling?
Diving more deeply into cross-selling, it revolves around broader customer experiences in e-commerce. It showcases your product range, making customers aware of other items that can be beneficial to them.
Amazon is a prime example of an e-commerce platform leveraging cross-selling effectively. They used the “Frequently bought together” and “Customers who bought this item also bought” sections to prompt additional customer purchases, that pair well with the primary purchase.
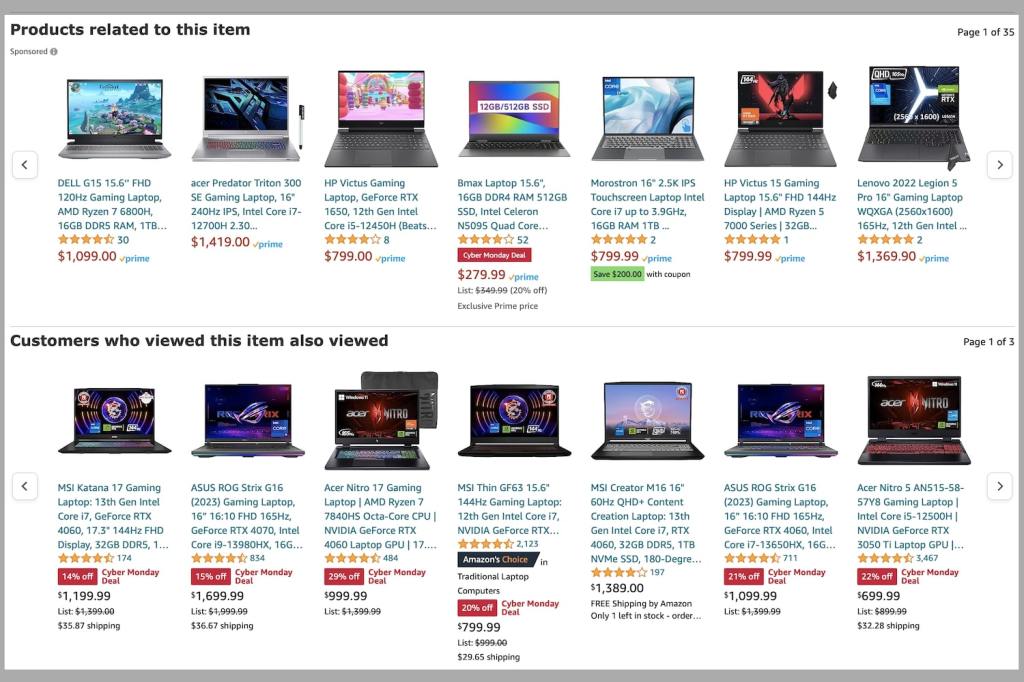
The benefits of cross-selling are multi-fold. Beyond driving higher order values, cross-selling can also greatly enhance the customer experience by suggesting relevant products, that they might have otherwise overlooked.
When done right, it can create a more convenient shopping experience. However, it does come with potential drawbacks. Excess or irrelevant cross-selling may overwhelm customers and trigger shopping cart abandonment. Hence, relevance and timing are crucial in this strategy.
To harness maximum advantage from cross sells further, e-commerce businesses should employ comprehensive customer behavioural data analysis and personalized product recommendations. This way, cross-selling can create a holistic shopping experience, concurrent customer engagement, and, most importantly, an impressive sales uplift.
What is Upselling?
Upselling is a sales technique where a seller persuades the customer to purchase more expensive items, upgrades, or other add-ons in an attempt to make a more profitable sale. It’s about enhancing the value that the customer gets from a product, thereby creating an opportunity for the business to maximize its profit on each transaction.
Taking an example from a real-world e-commerce giant, when you book a flight on Expedia, you will see suggestions for upgrades to business class or first class as a standard part of the checkout process. This is a classic example of upselling where the customers are enticed to spend more on their initial purchase.

The upselling strategy carries numerous benefits, including lifting the average transaction value, improving customer retention rates, and enriching the customer’s experience with the product or service. Nevertheless, just like cross-selling, it has its cons. If done overly or incorrectly, it could frustrate the customer and tarnish the shopping experience.
Therefore, it’s pivotal to position the upsell not as a sales push, but as a genuine recommendation that will enrich the customers’ experience or solve their problems more effectively.
Tip: Read our guide on the best upsell plugins you can use for WooCommerce.
When to Use Cross-selling and When to Use Upselling
Context is crucial when it comes to deploying either cross-selling or upselling. To understand the right scenarios for each approach, understanding your customer’s behaviour, product type, and other factors is crucial.
Upselling works effectively when a customer is not particularly price-sensitive and sees value in the purchase. Some common scenarios include when customers are shopping for luxury items, electronics, or services like travel and hospitality. Alternatively, cross-selling is effective if a product naturally pairs with other products.
For example, selling a camera? Cross-sell with SD cards or tripods. Also, cross-selling works well at the point of purchase or after the sale.
Remember that the best strategy to use would depend largely on what you sell, who your customers are, and how they shop. It’s an iterative process that may require constant testing and refining.
Strategies and Techniques for Effective Cross-selling and Upselling
When implemented properly, cross-selling and upselling strategies can significantly increase your ecommerce store’s average order value and overall revenue. Here are some actionable techniques for effectively implementing these strategies:
1. Understanding Your Customers
Before deciding which product to cross-sell or upsell, you need to understand your customers — their needs, preferences, buying habits, and price sensitivity. This will help you tailor your offers to match your customers’ needs, thereby increasing the chances of acceptance.
2. Leveraging Data Analytics
Data analytics plays a crucial role in cross-selling and upselling. By analyzing your customers’ previous purchases, browsing behavior, and demographic data, you can derive insights to personalize and optimize your cross-sell and upsell strategies.
Using data analytics, you can identify which products are frequently bought together, which products can be upgraded, and which customers are most likely to accept your upsell or cross-sell offers.
3. Offer Value, Not Just Products
Always focus on the additional value or benefits the customer will gain from the upsell or cross-sell. Instead of simply suggesting an additional product or a more expensive version, explain how the customer’s experience, satisfaction, or outcome will improve with your recommendation.
4. Timing is Crucial
Recognize the right time to cross-sell or upsell. Trying to sell additional products too early can be off-putting. Often, the best time for cross-selling is during the product selection process, while upselling is usually most effective at the point of sale.
5. Leverage Customer Reviews
Use customer reviews for similar or upgraded products. Positive reviews can motivate customers to consider purchasing additional items or higher-end models.

6. Personalization
Personalizing cross-sell and upsell offers is a great way to increase their effectiveness. Instead of employing a one-size-fits-all approach, use data about your customer’s browsing history, past purchases, and other behavior to make recommendations.
Remember, cross-selling and upselling strategies should benefit the customer and enhance their shopping experience. After all, a happy customer is much more likely to be a repeat customer and refer others to your online store.
Enhanced Ecommerce Tracking
Leverage the power of analytics to boost your store’s performance and maximize profits.
14-day, no-questions-asked money-back guarantee.
Case Studies on Cross-selling and Upselling
Examining real-world cases of successful cross-selling and upselling can provide valuable insights and actionable strategies. Here are a couple of examples:
1. Amazon: Frequently Bought Together
Amazon has used cross-selling very effectively with its Frequently Bought Together feature. The ecommerce giant uses big-data analytics to identify products that are often bought together and then suggests these products to customers. This strategy not only enhances the customer shopping experience by suggesting relevant products but also significantly increases the average order size.
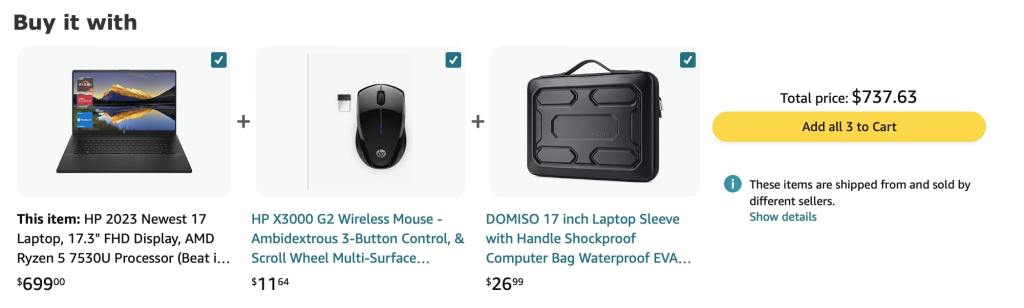
Key Learning: Customer data can be leveraged to provide personalized and relevant product suggestions, enhancing the shopping experience and boosting sales.
2. Apple: Higher-End Models and Add-Ons
Apple is famously effective at upselling. When purchasing an iPhone, customers are given options to upgrade to a model with more features or more storage capacity. Apple also cross-sells by suggesting complementary products like AppleCare (insurance) or AirPods (wireless earbuds).
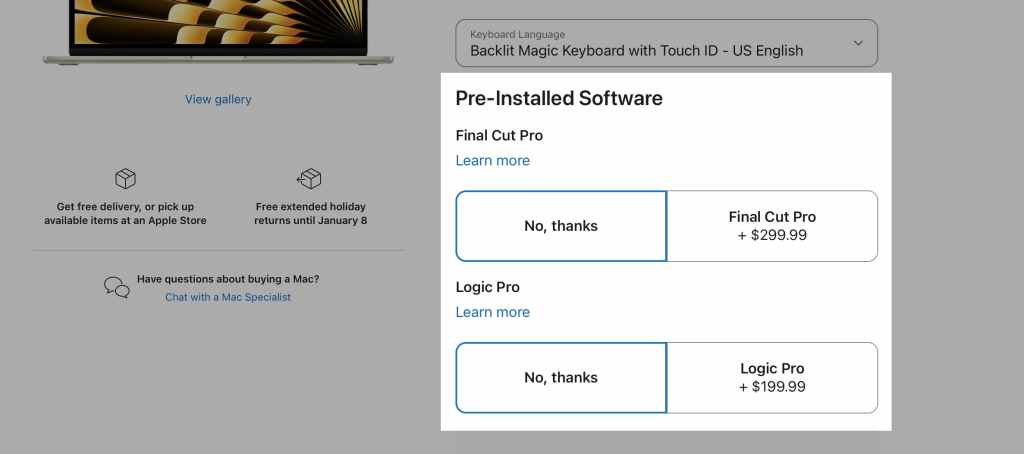
Key Learning: Upselling and cross-selling can enhance customer satisfaction if customers perceive elevated value in the higher-priced product or additional selections. Highlighting the added benefits or extended features can convince customers to spend more.
3. McDonald’s: Supersizing and Meal Deals
McDonald’s has famously mastered the art of upselling. Their most notable upselling technique is the offer to “supersize” meals. By promoting the perceived value of larger portions for a smaller price difference, many customers upgrade their meals.
Their “meal deals” function as cross-sells by bundling a main item, fries, and drinks together at a lower price as compared to purchasing each item separately.
Key Learning: Combining cross-selling and upselling strategies is an effective approach to increase average order value and promote the customer’s perceived value.
4. Best Buy: In-Store Kiosks and Service Add-Ons
Best Buy, a popular electronics retailer, effectively uses in-store touch-screen kiosks to showcase a range of accessories or warranties related to items in the customers’ carts. This cross-selling technique not only provides purchasing convenience but also increases the likelihood of customers purchasing additional items.
Best Buy also offers upsells in the form of installation services, extended warranties, or protection plans.
Key Learning: Seamless integration of cross-selling and upselling strategies within the shopping experience can greatly improve customer satisfaction and provide added convenience while increasing order value.
Measuring the Success of Your Cross-selling and Upselling Efforts
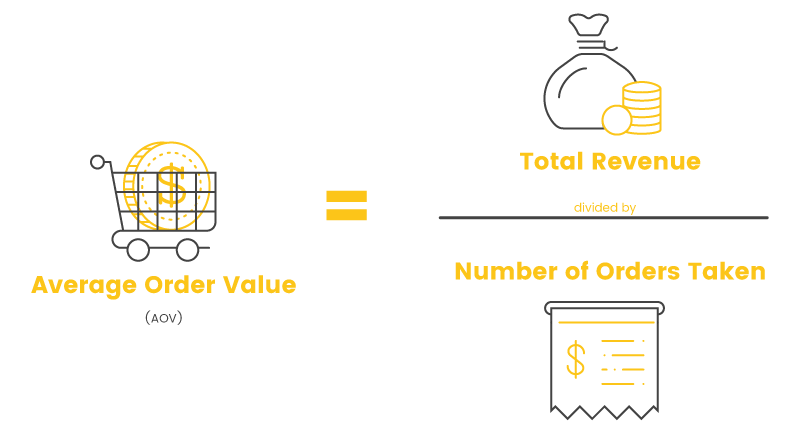
Understanding and implementing cross-selling and upselling is one thing, but evaluating their effectiveness is another essential factor. There are a few key metrics and KPIs to keep tabs on: Average order value (AOV), Conversion rate, Sales to existing and new customers both, Repeat purchase rate, and Customer lifetime value (CLTV).
The Average Order Value (AOV) calculates the average amount spent each time a customer places an order. An increase in AOV may indicate a successful upselling or cross-selling strategy.
The conversion rate measures the percentage of visitors who purchased out of the total number who visited your website.
Evaluating sales to existing customers and the repeat purchase rate can also provide insight into the success of your cross-selling and upselling efforts.
The Customer Lifetime Value (CLTV) is also a critical metric that measures the total revenue a business can reasonably expect from a single customer account.
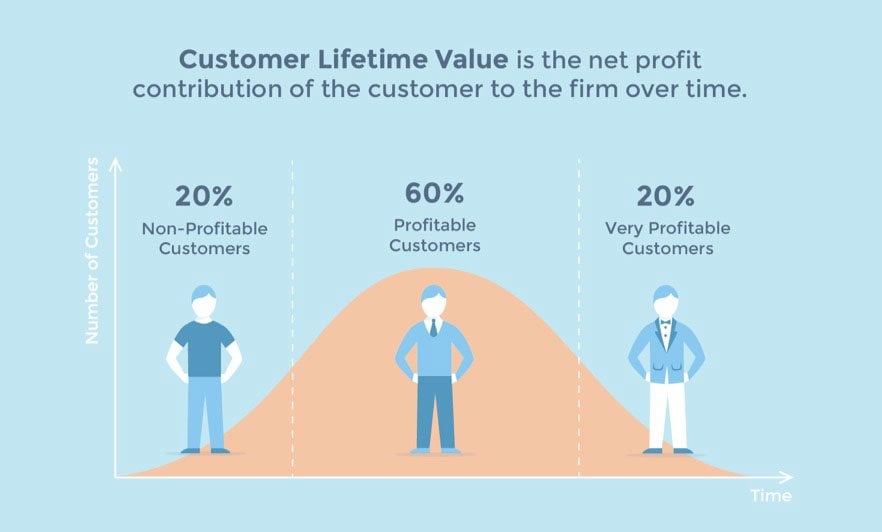
Regular assessments are important because these strategies need adjustment and refinement, and the results need to be measured against your set objectives to assess real progress.
Conclusion
As e-commerce continues to evolve and grow, cross-selling and upselling techniques emerge as powerful strategies that can significantly impact your business growth. Throughout this article, we have covered various aspects of these sales approaches, analyzed their benefits, and provided real-world examples.
By understanding the concept of upselling – an approach used to convince customers to purchase more expensive items, upgrades, or other add-ons – merchants can potentially maximize their profit on each transaction. On the other hand, cross-selling involves offering additional products that complement the customer’s primary purchase, thereby increasing average order value and customer satisfaction with repeat purchases.
Both approaches are instrumental in choosing the right strategy based on customer behaviour, product type, and other factors. The key to success lies in incorporating data analytics to personalize and enhance your customers’ shopping experience effectively.
Learn from the successes of industry giants like Amazon and McDonald’s, which have harnessed these strategies to increase revenue and customer loyalty. To measure the effectiveness of your cross-selling and upselling efforts, keep an eye on crucial KPIs such as average order value, conversion rate, and customer lifetime value. Regularly adjust and refine your strategies, keeping the focus on providing genuine value to your customers.
In conclusion, e-commerce businesses must view cross-selling and upselling techniques as essential elements of customer journey that drive growth rather than just quick sales tactics. With the right approach and continuous improvement, your e-commerce business can experience increased customer satisfaction, better overall customer relationships, and of course, higher profitability. Embrace the strategies outlined in this article, adapt them to your unique circumstances, and take your e-commerce growth to new heights.
FAQs
What is the difference between upselling and cross-selling?
Upselling and cross-selling are two sales strategies aiming to maximize each transaction’s value. However, they differ in approach. Upselling involves convincing a customer to buy a more expensive version of the product they’re considering or additional features or upgrades that increase the sale value. For instance, if a customer is looking at a basic software package, offering them a premium package with more features would be upselling.
Cross-selling, on the other hand, encourages customers to buy related or complementary items. The goal here is not to increase the value of the individual product but to encourage customers to increase the overall value of the sale by adding more products to the transaction. A great example of cross-selling is a cable television provider that also offers internet and phone services to its customers; getting a customer to subscribe to all three services is an act of cross-selling.
What are two examples of cross-selling & two examples of upselling?
Cross-selling examples can be seen in many businesses. A common example of cross sell products would be seen in a restaurant, where a waiter suggests a wine that pairs well with the ordered meal. Another example is evident in the e-commerce industry, where, during the checkout process, online stores often suggest related items to the product in the cart.
Examples of upselling are also recurrent; a classic example is seen in the airline industry, where business-class or first-class upgrades are offered to economy-class passengers. Another example is in the electronics industry, where a customer intending to buy a laptop may be persuaded to purchase a more expensive model with superior performance and features.
What is the best definition of cross-selling?
Cross-selling is a sales strategy in which the seller encourages the customer to purchase related or complementary products or services to what they’re currently buying. The intention of cross selling techniques is to increase the value of the purchase, improve customer satisfaction, and maximize profitability. Cross-selling can occur during the initial sale, at the point of purchase, or even after the sale has been made. It’s a strategic move used to build customer loyalty and to create convenience by providing related products in one place.
What is an example of cross-selling in B2B?
Cross-selling can be effectively implemented in a Business to Business (B2B) environment as well. A cloud services provider, for example, could cross-sell a combination of services to a customer initially interested in just one service. The customer may have originally planned to purchase web hosting services, but the B2B provider could cross-sell complimentary services like domain registration, email hosting, and cloud storage. This can be beneficial to the customer as they get a comprehensive solution in one place, and for the provider, as it increases their overall deal value.
Enhanced Ecommerce Tracking
Leverage the power of analytics to boost your store’s performance and maximize profits.
14-day, no-questions-asked money-back guarantee.